机器学习
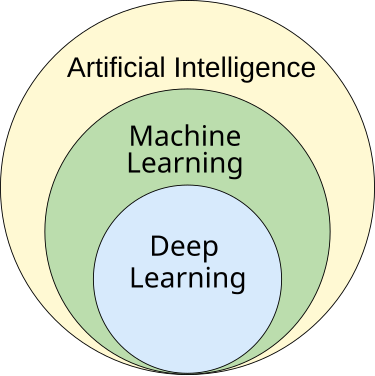
definition
机器学习(ML)是人工智能的一个研究领域,关注于开发和研究能够从已有数据中学习并推广到未见数据,从而无需明确指令就能执行任务的统计算法。在机器学习的一个子学科中,深度学习领域的进展使得神经网络——一种统计算法——在性能上超越了许多之前的机器学习方法。
统计学和数学优化(数学规划)方法是机器学习的基础。数据挖掘是一个相关的研究领域,专注于通过无监督学习进行探索性数据分析(EDA)。
从理论角度来看,大概近似正确学习为描述机器学习提供了一个框架。
history
机器学习一词由 IBM 员工、计算机游戏和人工智能领域的先驱亚瑟·塞缪尔于 1959 年提出。在这个时期,也使用了同义词“自教学计算机”。
最早的机器学习程序出现在 20 世纪 50 年代,当时亚瑟·萨缪尔发明了一个计算机程序,用于计算跳棋双方获胜的概率,但机器学习的历史可以追溯到人类数十年来研究认知过程的愿望和努力。1949 年,加拿大心理学家唐纳德·赫布出版了《行为的组织》一书,书中介绍了一种由神经细胞之间特定相互作用形成的理论神经结构。赫布的神经元相互作用模型为人工智能和机器学习算法在节点(计算机用于通信的人工神经元)下如何工作奠定了基础。其他研究人类认知系统的研究者也促进了现代机器学习技术的发展,包括逻辑学家沃尔特·皮茨和沃伦·麦克洛克,他们提出了早期的神经网络数学模型,以形成模拟人类思维过程的算法。
Modern day Machine Learning algorithms are broken into 3 algorithms types: Supervised Learning Algorithms, Unsupervised Learning Algorithms, and Reinforcement Learning Algorithms.
- Current Supervised Learning Algorithms have objectives of classification and regression.
- Current Unsupervised Learning Algorithms have objectives of clustering, dimensionality reduction, and association rule.
- Current Reinforcement Learning Algorithms focus on decisions that must be made with respect to some previous, unkown time and are broken down to either be studies of model based methods, and model free methods.
theory
学习者的一个核心目标是泛化其经验。在此文中,泛化是指学习机器在经历学习数据集后,能够对新未见过的示例/任务进行准确执行的能力。训练示例来自某个通常未知的概率分布(被认为是发生空间的代表),而学习者必须构建一个关于这个空间的通用模型,使其能够在新情况下产生足够准确的预测。
机器学习算法及其性能的计算分析是理论计算机科学的一个分支,通过概率近似正确学习模型(probably approximately correct learning model)属于计算学习理论(computational learning theory)。由于训练集是有限的且未来是不确定的,学习理论通常不会提供算法性能的保证。相反,性能的概率界限相当常见。偏差-方差分解(bias–variance decomposition)是量化泛化误差(generalisation error)的一种方法。
在泛化性能方面,假设的复杂度应与数据底层函数的复杂度相匹配。如果假设的复杂度低于函数,则模型对数据欠拟合。如果相应增加模型的复杂度,则训练误差会下降。但如果假设过于复杂,模型容易过拟合,泛化能力会变差。
applications
There are many applications for machine learning, including:
- Agriculture
- Anatomy
- Adaptive website
- Affective computing
- Astronomy
- Automated decision-making
- Banking
- Behaviorism
- Bioinformatics
- Brain–machine interfaces
- Cheminformatics
- Citizen Science
- Climate Science
- Computer networks
- Computer vision
- Credit-card fraud detection
- Data quality
- DNA sequence classification
- Economics
- Financial data analysis
- General game playing
- Handwriting recognition
- Healthcare
- Information retrieval
- Insurance
- Internet fraud detection
- Investment management
- Knowledge graph embedding
- Linguistics
- Machine learning control
- Machine perception
- Machine translation
- Material Engineering
- Marketing
- Medical diagnosis
- Natural language processing
- Natural language understanding
- Online advertising
- Optimisation
- Recommender systems
- Robot locomotion
- Search engines
- Sentiment analysis
- Sequence mining
- Software engineering
- Speech recognition
- Structural health monitoring
- Syntactic pattern recognition
- Telecommunications
- Theorem proving
- Time-series forecasting
- Tomographic reconstruction
- User behaviour analytics